Understanding how contactless payments work
At Clairvoyant, we have performed multiple Big Data and Cloud implementations for our clients and accelerated their digital transformation journeys. Many of these projects are focused on improving operational efficiency Financial Data Processing and Reporting.
This blog will provide readers an overview of NFC and Contactless payments and their relevance in the Financial world.
The rise in Contactless Payments
With the advent of mobile payments, we see a shift from a cash-driven economy to a more cashless economy. Faster data processing, enhanced data security, and greater customer-centric features have led to a boom in mobile payment applications. Also, due to the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic, customers now prefer contactless payments to avoid disease transmission via touch at POS terminals at store checkouts. Overall, these factors have highly contributed to an increase in contactless payments. NFC is the technology that drives these payments.
What is NFC, and how it works?
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a wireless communication technology introduced in the early 2000s that enables the transfer of data between 2 NFC-enabled devices placed closely using radio-frequency. It enables 2-way communication. When 2 NFC-enabled devices come within 2 inches of each other, magnetic induction is activated. They exchange data over a 13.56 MHz radio spectrum, which only works when the chips are very close together. The maximum transferring speed is 424kbps.
Modes of Transfer in NFC
-
Peer to Peer- This mode facilitates the exchange of data between 2 NFC-enabled devices and is used mostly for file transfers between 2 devices.
-
Reader/Writer Mode- In this mode, one device acts passive and another active. The active device reads data from the passive one. This mode is used in contactless Debit/Credit Cards.
-
Card Emulation Mode- Mobile payment apps use this mode; the device functions as a virtual credit card.
Applications of NFC in Payments
When customers view the contactless or wave signal in the POS terminal, they know that the card reader is NFC-enabled and can pay using NFC-enabled apps or cards.
In payments, NFC technology is used in 2 ways:
-
Mobile Apps- Google, Samsung, and Apple Pay
-
Contactless Credit and Debit Cards- Visa, MasterCard, Amex
How to Make Contactless Payments?
-
The first method - is through mobile apps. The customer has to open the NFC-enabled payment app and choose a payment method. Once the customer has chosen the payment type, they simply wave or tap their electronic device over the NFC-enabled POS terminal to complete the transaction. NFC payment transactions between a mobile device and a POS terminal use ISO/IEC 14443 standard. A wallet on an NFC-enabled mobile device is a software application stored on the mobile phone that manages and initiates payments. This initiates an electromagnetic induction link between the device and the POS terminal. Each NFC transaction generates a one-time unique code, and the user’s card details are stored in an encrypted format in wallets. The distance should be less than 4 cm, and the technology uses a radio frequency of 13.56MHZ.
-
The second method - is via the use of NFC-enabled contactless cards. Customers can simply wave or tap over the card reader, and the transaction will happen. The card reader is the active device and reads the card details from the passive NFC-enabled card. There is no need for contact between the physical card and the card reader.
Note - Ordinary POS systems can’t process these NFC transactions at the shops. Hence, for both the ways mentioned above of NFC payments to be accepted, there must be an NFC-enabled card reader.
Most Popular NFC Mobile Applications
-
Google Pay
-
Apple Pay
-
Samsung Pay
How is card data stored in NFC-enabled apps?
Sensitive information can be secured in digital wallets in 2 ways:
-
Secure Element (SE) — It is device-based and can be considered as a smart card in the phone which is isolated from tampering by a restricted access interface. It stores sensitive information related to cards. SE operates by using tokenisation embedded in the device itself. The user’s generated credit card token is stored in SE.
-
Host Card Emulation (HCE) — It is cloud-based and allows the device to act as a card on an NFC-enabled device. In HCE, the users’ credit card details are stored in the cloud servers of the mobile payment app.
In both methods, the customer’s card details are only provided once during the initial setup.
In Google Pay, Google stores the card details on its cloud servers and a virtual card is issued for the customer's device. During the payment transaction via Google Pay, the customer’s device only transmits this virtual card, and nowhere is the actual card information transmitted making the process highly secure.
Apple employs a different mechanism known as Tokenisation. Here, once the customer uploads the card details into Apple Pay, Apple sends the card details to the issuing bank of the customer. The issuing bank confirms the account details and sends a device and card-specific token called the Device Account Number (DAN). This token is stored on a secure chip on the mobile device and resembles a credit card number. This DAN is only transmitted when any purchase is made by the customer using Apple Pay to the merchant and nowhere in the transaction flow are the actual card details exposed.
Advantages of Contactless Payments
-
Great Customer Experience — Contactless payment transactions are hassle-free. Customers don’t have to spend more time at POS checkouts as they just have to wave their mobile devices or Cards at the POS terminal without the need to type in their PINs.
-
Safer Transaction — Tap-to-pay technology is very reliable and secure than the other forms of payment. The card details are stored in the form of tokens, and during a transaction, the tokens are sent over the web. In case of any hacker attack, the actual credit card information is nowhere available while data is transmitted.
-
Faster Processing — Contactless payment processing is quite fast, and it takes only a few seconds for the payment-related information to be transmitted between the payment device and the POS reader.
Challenges in Contactless Payments
-
Need for NFC-enabled card readers — The traditional POS systems in shops can’t accept payment via NFC-enabled cards or apps. Such shop owners need to upgrade their POS systems to accept NFC payments via contactless cards or apps. Unless the retailers or shop owners upgrade their POS systems, NFC-enabled payments can’t be facilitated, and customers will have to use the swipe or dip methods.
-
NFC-enabled devices — Not all mobile devices are NFC-enabled. Also, NFC-enabled devices are priced higher compared to their counterparts- the non-NFC smartphones.
-
Transaction limitations — As NFC payments do not require a signature or a PIN, in order to avoid any fraudulent transactions, there are limitations to the maximum purchase amount or number of withdrawals that can be made in a day. This amount is dependent on the card issuer and the sponsoring bank’s policy.
Conclusion
The contactless payments industry has been seeing a tremendous boom in recent years. There is a growing demand for contactless Cards, and according to a report by ABI Research, the number of contactless cards shipped in the US is set to reach 196.8 million in 2021. The overall global contactless payment market is expected to register a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of around 20.01% during the period between 2020 and 2027.
With the world moving towards digitalization, NFC technology and Contactless payments are reshaping the fintech landscape by driving the digital cashless economy.
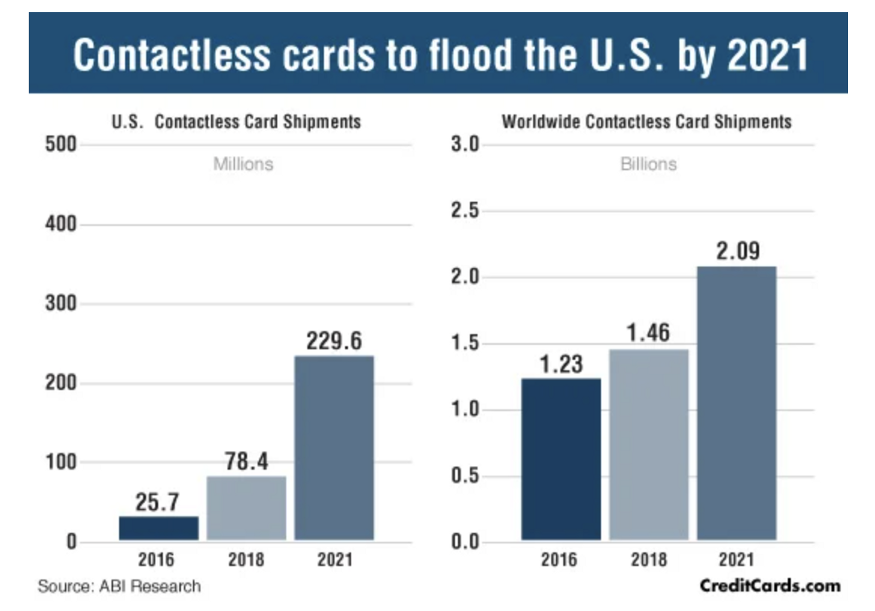 Source: ABI Research / Creditcards.com
Source: ABI Research / Creditcards.com
For more information or further queries, please email us at hello@clairvoyantsoft.com or call us at (623)282–2385. Learn more at: https://www.clairvoyant.ai
References -
Info on Credit Card shipped-https://www.creditcards.com/credit-card-news/topics/research-and-statistics/
Info on Contactless Payment Market-https://www.precedenceresearch.com/contactless-payment-market
Info on NFC-https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Near-field_communication
To find the best cloud based services, reach out to us at Clairvoyant and fulfill all your business needs.
