Serialization means converting the state of an object into a byte stream so that it can be used to construct copies of the object when needed.
Deserialization is converting the byte stream (serialized object) into a copy of the object in memory.
In the case of Apache Kafka, serialization/deserialization becomes important as it stores and transfers data as a byte array.
The Apache Kafka provides a Serde interface, which is a wrapper for serializer and deserializer of a data type. Kafka provides an implementation for several common data types. These implementations are present in kafka-cleints jar.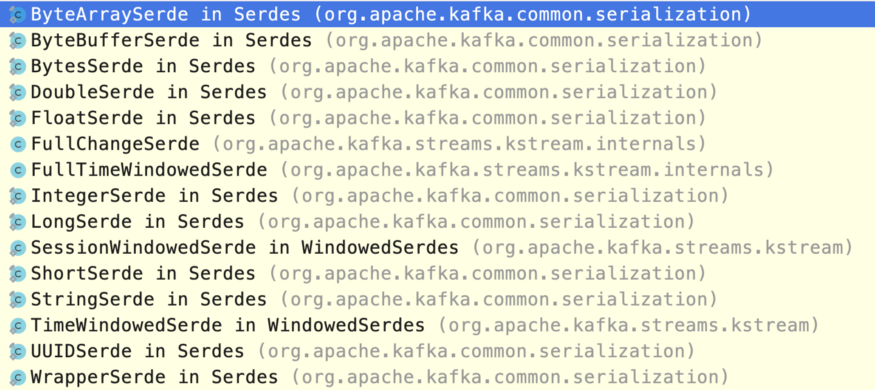 Kafka Provided Implementations of Serde interface
Kafka Provided Implementations of Serde interface
Kafka also provide a factory called Serdes for creating those implementations. For example, if we want to create the Serde for String type, we can do that as follows:
//Creates a String serde Serde<String> stringSerde = Serdes.String(); // Creates a Long serde Serde<Long> longSerde = Serdes.Long();
Since these implementations have a serializer and deserializer for a data type we don’t have to define key serializer/deserializer and value serializer/deserializer every time we want to use Serde.
Writing a Custom Serde
Although Kafka provides several Serde implementations (String, Long, Integer, etc.) out of the box, we need to write our own implementations for more complex data types(e.g., User-defined data types). In this section, we will define the steps to create a custom implementation:
-
First, We need to define our own implementation of Serializer<T> and Deserializer<T> interfaces.
-
Then, we can use the utility method Serde<T> serdeFrom(final Serializer<T> serializer, final Deserializer<T> deserializer) from Serdes to get the customSerde<T>.
Let us take an example of a data type called Book. We need to implement a custom Serde for this.
public class Book {
private String isbnNumber;
private String title;
// Getter, Setter and other methods omitted for brevity
}
Implementing a Serializer for Book
The Serializer interface provides the below three methods which can be overridden:
/**
* Configure this class.
* @param configs configs in key/value pairs
* @param isKey whether is for key or value
*/
void configure(Map<String, ?> configs, boolean isKey);
/**
* Convert {@code data} into a byte array.
*
* @param topic topic associated with data
* @param data typed data
* @return serialized bytes
*/
byte[] serialize(String topic, T data);
/**
* Close this serializer.
*
* This method must be idempotent as it may be called multiple times.
*/
@Override
void close(); // This is an inherited method from Closeable
Here we are going to override the serialize method. Below is the code for the BookSerializer:
package com.clairvoyant;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.apache.kafka.common.errors.SerializationException;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer;
/**
* created by imteyaza-1lm on 2019-04-23
**/
public class BookSerializer implements Serializer<Book> {
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs, boolean isKey) {
}
@Override
public byte[] serialize(String topic, Book data) {
if (Objects.isNull(data)) {
return null;
}
try {
return objectMapper.writeValueAsBytes(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SerializationException("Error serializing message",
e);
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
}
The ObjectMapper class from Jackson.
Implementing a Deserializer for Book
The Deserializer interface provides the below 3 methods which can be overridden:
/** * Configure this class. * @param configs configs in key/value pairs * @param isKey whether is for key or value */ void configure(Map<String, ?> configs, boolean isKey); /** * Deserialize a record value from a byte array into a value or object. * @param topic topic associated with the data * @param data serialized bytes; may be null; implementations are recommended to handle null by returning a value or null rather than throwing an exception. * @return deserialized typed data; may be null */ T deserialize(String topic, byte[] data); @Override void close(); // This is an inherited method from Closeable
We will only override the deserialize method here as shown in the code below:
package com.clairvoyant;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.apache.kafka.common.errors.SerializationException;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Deserializer;
/**
* created by imteyaza-1lm on 2019-04-23
**/
public class BookDeserializer implements Deserializer<Book> {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs, boolean isKey) {
}
@Override
public Book deserialize(String topic, byte[] bytes) {
if (Objects.isNull(bytes)) {
return null;
}
Book data;
try {
data = objectMapper.treeToValue(objectMapper.readTree(bytes),
Book.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SerializationException(e);
}
return data;
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
}
Once we have implemented the Serializer and Deserializer interfaces, we can create the custom Serde for Book:
Serde<Book> bookSerde = Serdes.serdeFrom(new BookSerializer (), new BookDeserializer());
Now, we can use this BookSerde as follows:
Serde<Book> bookSerde = Serdes.serdeFrom(new BookSerializer
(), new BookDeserializer());
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("application.id", "book_app");
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092,localhost:9093");
props.put("key.serializer", bookSerde.serializer().getClass());
props.put("value.serializer", bookSerde.deserializer().getClass());
Learn how to write a Custom Partitioner for Apache Kafka in our blog here. To get the best data engineering solutions for your business, reach out to us at Clairvoyant.