The right cloud architecture model can transform the way you do business and help you gain a competitive edge in the market. Enlisted below are different ways you can choose your cloud delivery model.
Technology has evolved by leaps and bounds over the last decade, allowing businesses along the way to reap the benefits of streamlined, cost-efficient operations. At the crux of this digital transformation is the rise of cloud computing technology, which has proven to be a game-changer for businesses across different geographies and sizes. Cloud has proven to achieve resilience and scale through horizontal scaling, distributed processing, and automating failed components.
Cloud computing architectures have matured in an extremely short span of time and made readily acceptable to the changing needs of the IT sector. They basically comprise of two parts, i.e., the front-end and the back-end. The front end is the end utilized by the user or client, e.g., browser or an app created by the company itself; The back-end is managed by the host and typically contains extensive data storage facilities, virtual machines, security systems, and servers. Both ends connect with the means of the internet.
The back-end system comprises three main cloud delivery models:
-
Software as a Service (SaaS)
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The main difference in these models is how much of the IT stack the vendor will manage to how much the customer will manage. Choosing the right cloud service model can be challenging and depends heavily on your business and technology service requirements.
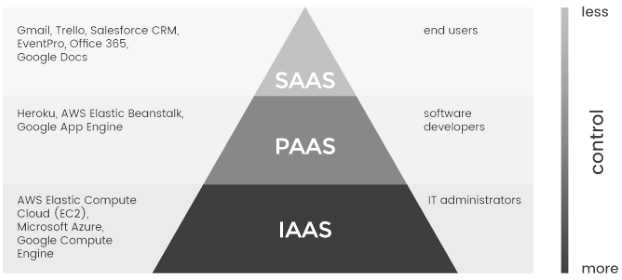
1. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Saas provides clients with the ability to use software applications over the internet via (pay-per-use) subscription basis. The entire IT stack is managed by the vendor so there is no real need for an internal IT team to manage it. This is appealing to smaller firms that do not have a large dedicated IT team.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform where clients can deploy their own applications and host them. The client is free from the hassles of setting up infrastructure, managing storage, servers, network, etc. The vendor supplies full infrastructure for app development while developers are in charge of the code.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides basic computing resources such as processing power, data storage and networking components. The client has complete control over the storage, operating system, deployed applications and network components such as firewalls and load balancers.
In addition to the cloud delivery models stated above, there are essentially three cloud deployment models, namely:
-
Public Cloud
-
Private Cloud
-
Hybrid Cloud
Public Cloud
The cloud infrastructure in the public cloud is in the service provider's premises. The client lacks control over the geo-location of the cloud infrastructure. Public clouds often provide an elastic, cost-effective means to deploy solutions, to leverage the provisioning and releasing characteristics of the shared computing resources pool.
Private Cloud
A particular organization or enterprise solely owns a private cloud. It offers great levels of security and control, especially for companies that need top data managed services and uptime requirements. It is also the preferred choice for companies that need to administer their host applications and other applications used by their clients.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines a public cloud and a private cloud that facilitates the interoperability of the applications deployed on both clouds. The rationale is to reap the best benefits from both flavors. In this model, users typically deploy non-sensitive applications and data to the public cloud while keeping sensitive services and data in their control in the private cloud.
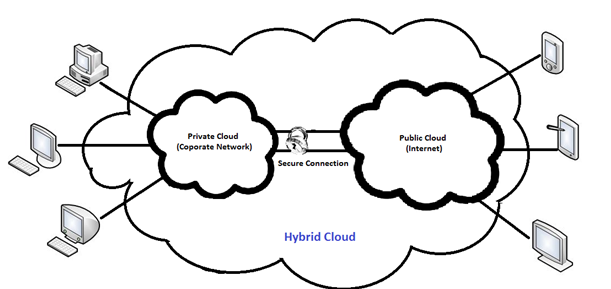 Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud
Cloud Management
Cloud Management solutions within an architectural setup are crucial to help an organization increase visibility into and across public and private cloud infrastructures. These platforms give customers a way to manage cloud cost, usage, security, and real-time performance monitoring from a single interface. The Cloud Management Platform contains all of the base services needed to automate and optimize the private and public clouds.
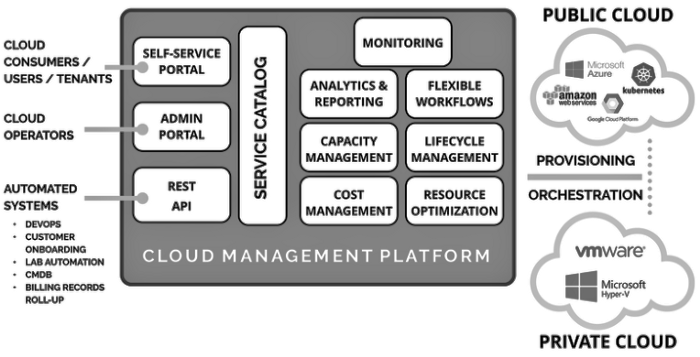 Cloud Management Platform. Source: Embotics.com
Cloud Management Platform. Source: Embotics.com
The services included within a cloud management platform are as follows:
Built-in Cloud Automation and Orchestration: Built-in orchestration provides a mechanism to link and automate the provisioning for various services your organization requires, with permissions oversight and policy enforcement.
Monitoring: The monitoring tool provides metrics using customizable dashboards and alerts. Organizations can rapidly detect erroneous activity by testing networks and infrastructure regularly, securing networks from potential threats.
Analytics and Reporting: Built-in analytics provides cost information and best practices that are out-of-the-box, easy to consume, with deep reporting data. You could deliver billing reports to your business users from minutes after installation showing actual IT services costs.
Cost Management: The cloud cost management tool provides cost visibility, actionable cost savings, and cloud cost comparisons. It helps simplify budget tracking and spending analysis to reduce waste and lower overall costs in the cloud.
Flexible Workflows and Life-cycle Management: Easily customizable and extensible through a web-based user interface, it addresses your IT and business needs. Organizations can reduce manual steps and improve the efficiency of their workflows rapidly at a considerably lower cost by leveraging any pre-existing scripts or using workflow building blocks.
Resource Optimization and Capacity Management: An important but often-overlooked aspect of cloud cost management is the awareness of what you have running. The best way to avoid unused resources is to prevent them from being created. Resource optimization tools alert you to anomalies, such as a database that is not attached to any applications or a virtual server that no one has accessed recently.
APIs For Interaction And Collaboration: APIs play many important roles in cloud computing. They are a means for products and services to communicate effectively through a documented interface. APIs can integrate third-party applications and other workloads into the cloud. APIs can speed up the platform access and direct more efficient platform security management. They make handling analytics an easy task. However, the most important aspect is that APIs ensure data portability and interoperability.
Conclusion
Modern cloud architectures can have several facets that combine workloads, microservices, and platform services, resulting in more agile, iterative delivery. Enterprises increasingly want to take advantage of the flexibility and choice of multiple cloud offerings to use the best cloud services while achieving satisfactory cost reduction benefits.
Each business is unique and requires expertise in designing and maintaining the cloud. As a trusted partner, Clairvoyant offers a broad set of cost-effective cloud solutions to improve business efficiency in a highly secure manner. We adopt modern cloud architectures to deliver the best experience to customers and benefit from greater agility and faster time to market. You get a comprehensive cloud management solution that allows you to implement all of your cloud management strategies in one place. To get the best cloud based services, reach out to us.
References:
Mcintyre D, Nov 2018, SaaS vs IaaS vs PaaS. Retrieved from: https://devworld.io/saas-vs-iaas-vs-paas/
Choudary A, May 2019, Cloud Computing Services: A Deeper Dive Into Cloud Computing. Retrieved from: https://www.edureka.co/blog/cloud-computing-services-types/